One of the feature enabled by OOP encapsulation is component reuse i.e, being able to not repeat implementations. Many mechanisms have been implemented in almost all languages with OOP: C++, Java, Python, Ruby...
One of the key difference is how two objects share their implementation. For example, Javascript is prototype-based, but almost all others languages are class-based.
U lets you choose the best paradigms. In U, the way objects share their implementation is simply called a link. There are three links:
- Inheritance
- Composition
- Aggregation
They differ by their rules:
- creation:
- compile-time: object cannot be modified once compiled;they are static;
- run-time: object can be modified by adding attributes or methods; they are dynamic.
- deletion: does the parent deletion, delete childs too?
- private sharing: does childs have access to parent private data?
| Link | Creation | Deletion | Private Sharing | Keyword |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inheritance | ugo | yes | yes | ::is_a |
| Composition | ugo | yes | no | ::has |
| Aggregation | ugo | no | no | ::holds |
ugo means you can specify object creation behavior in ugo. By default, object cannot be changed at run-time, but you can enable it. When object can be modified at run-time, there are called be opened objects(keywords ::oopen).
For example:
::A :Person, :name: @string
::A :Dev,
:is_a: @Person # Inheritance
:has: {:skills: @Skills }, # Composition
:holds: {:cart: ... } # Aggregation
:eve : ::a @Dev
eve.name # Inheritance
eve.skills.count # Composition
eve.cart # Aggregation
This example is depicted in figure below.
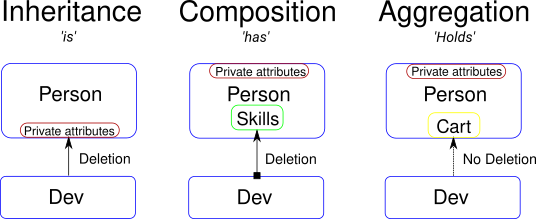
Inheritance provides the simplest syntax hiding the implicit Person link. But for large or sensitive projects, Composition provides better controls over private attributes sharing.
Root Class¶
All classes derive from a common class: the @Root class. Root provides basic attributes and methods for all objects, like comparison and inspection methods.
Class Graph¶
Class Graph is the term used to describe links between objects. In the above example, the Class Graph is simple the chain Developer -> Person -> @Root. The arrow shows the method lookup path.
For example, Class Graph lets us easily visualize internal mapping with class diagrams.
Method Lookup¶
U walks the Class Graph to retrieve a specific method.